Ancient Egyptian Mythology
Ancient Egyptian mythology has a religious and cultural structure ranging from the prehistoric period of Egypt to the Roman period. Egyptian mythology encompasses many elements such as gods, goddesses, creation myths, and life after death. The main themes of this mythology include the creation of the universe, royal authority, and life after death. The ancient Egyptians used this mythology to explain natural events and important events in their societies.
In Egyptian mythology, there are several myths about the creation of the universe. One of the most well-known creation myths is Heliopolis. According to this myth, the chaos originally contained a primitive water mass called Nun. This chaos, Atum, the first god, appeared. Atum created Su (the air god) and Tefnut (the goddess of goodness and moisture) as a self-created god. She gave birth to Shu and Tefnut, Geb (the earth god) and Nut (the goddess of heaven). By the merger of Geb and Nut, Osiris, Isis, Seth, and Nephthys were born.

These gods are known as the Ennead, who played an important role in Egyptian mythology. Osiris was the first king of Egypt and the god of death. Isis is the goddess of magic and fertility. Seth is the god of chaos and destruction. Nephthys is a protective goddess. The murder of Osiris by Seth, and the resurrection of him by Isis, starts the cycle of death and rebirth.
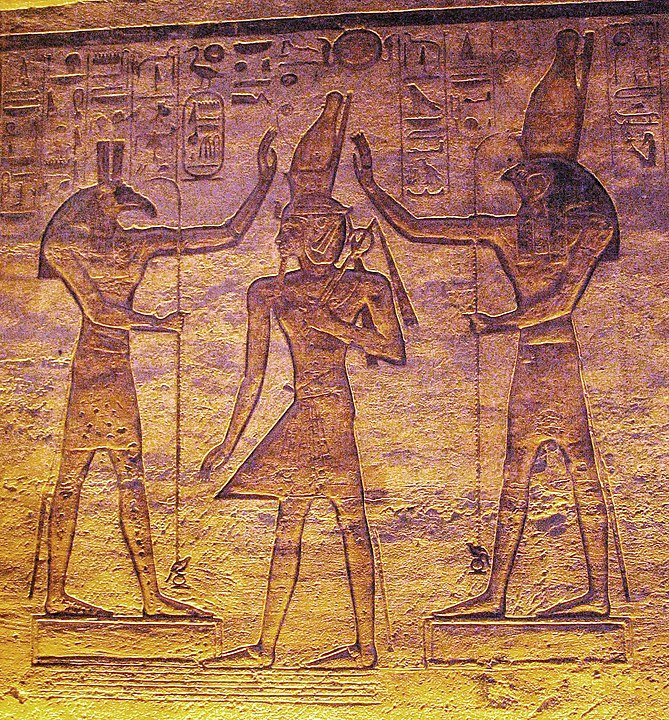
There are countless gods and goddesses in Egyptian mythology, the most important of which are Ra, Osiris, Isis, Horus, Seth, Anubis, and Hathor.
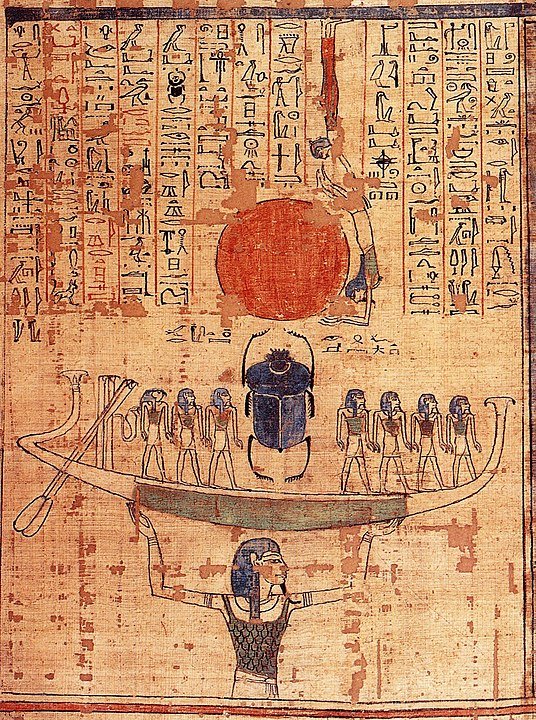
Ra: The sun god Ra is one of the most important gods in Egyptian mythology. Ra is usually described as a human body and the head of the shaikh. Ra travels in a boat every day in the sky and spends the night in the underworld. Ra’s cycle symbolizes the cycle of life and death.
Osiris: The god of the dead and ruler of the underworld, Osiris is a symbol of rebirth and blessing. Osiris is a representative of justice and order in Egyptian mythology. After he dies, he rules the underworld and plays an important role in the trial of the dead.
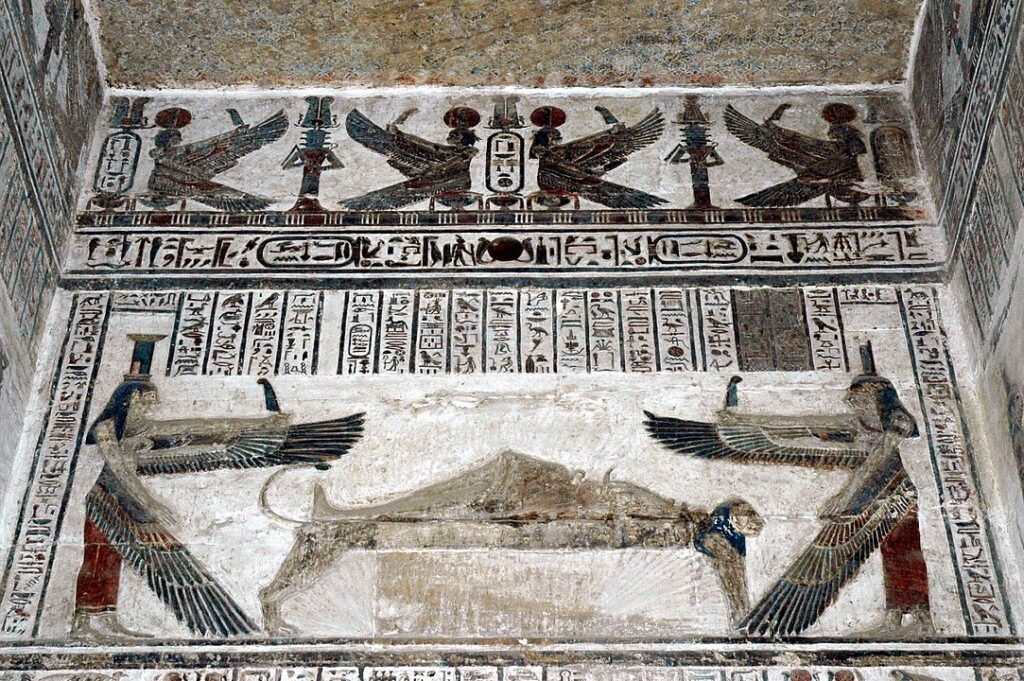

Isis: A goddess of magic, motherhood and fertility, Isis is known for having the power to revive her brother and wife Osiris. Isis is also the guardian of the kingdom and motherhood.
Horus: Horus, the god of the sky, is usually depicted as a man headed by a shahin or shahin. Horus is the son of Osiris and Isis, and fought with Seth to avenge his father. Horus is considered the guardian of the pharaohs.
Seth: The god of chaos, storm and destruction, Seth represents opposite forces in Egyptian mythology. Seth kills his brother Osiris, causing chaos, but is eventually defeated by Horus.
Anubis is known as the mummification and patron savior of the dead. He is usually described as a chakal headed person. Anubis takes the souls of the dead to the underworld and helps them judge.
Hathor: The goddess of love, beauty, and music, is often depicted as a cow-headed woman. Hathor is also the goddess of fertility and motherhood.
In Egyptian mythology, death and life after death are of great importance. The Egyptians believed that life after death continued, and they prepared their dead for this belief. The mummification was done to ensure the preservation of the body and the existence of the soul after death.
There are several stages that the soul must go through after death. One of them is the trial before Osiris. The deceased, his heart is struck with “Maat’s Tiger”. If his heart is as light as a hair, the deceased is admitted to paradise-like Aaru fields. However, those with heavy hearts are defeated by Ammit and their souls are destroyed forever.
In Egypt, temples and rituals were important places for worshiping and worshipping the gods. Temples such as Karnak, Luxor and Abu Simbel are the largest and most magnificent buildings dedicated to the gods. In these temples, priests offered sacrifices to the gods, prayed and performed various rituals.
The priests cleaned, clothed and fed the statues of the gods daily. These rituals were considered necessary to maintain the power and protection of the gods.
Ancient Egyptian mythology is a rich mythological system that deeply influences the religious, cultural and social structure of society. Through gods and goddesses, mythological stories and rituals, the Egyptians sought to understand life, death, and the order of the universe. These mythological accounts are an important source for understanding Egypt’s historical and cultural heritage.



